Elastic Social Manual / Version 2406.0
Table Of ContentsThe Elastic Core message queue is based on the idea that method calls (called tasks) may be deferred (that is, queued) to a later point of time where they can be processed concurrently by a pool of worker applications. It is ensured that a task is executed at least once. On errors the task is automatically retried by another worker until an error count limit is reached.
The TaskQueueService persists its information in the same MongoDB as the
ModelService and uses the same mapping algorithm to store the arguments of the method
calls.
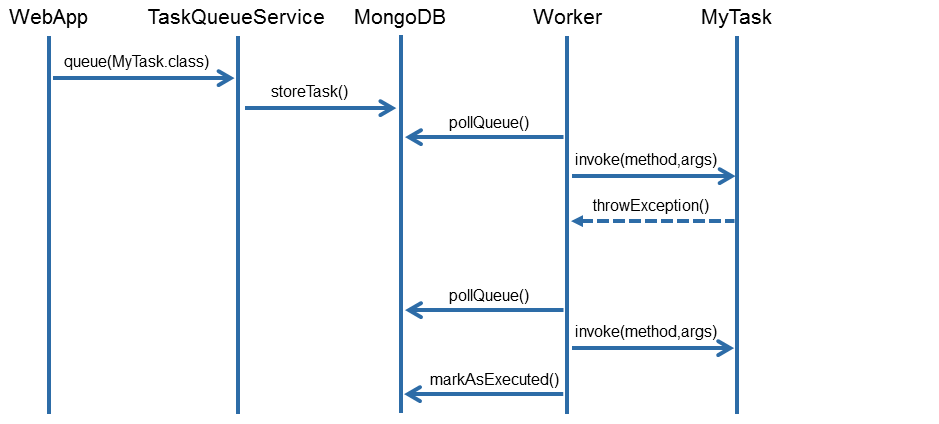
A typical method call sequence when using the TaskQueueService looks like this:
Creating task queues
To create a TaskQueue with the name mytasks, define a
TaskQueueConfiguration like this:
@Named
public class MyTaskQueues implements TaskQueueConfiguration {
@Inject
private TaskQueueConfigurationBuilder builder;
public Iterable<TaskQueue> getTaskQueues() {
return builder.
configure("mytasks").
build();
}
}
Example 4.10. TaskQueueConfiguration
Executing tasks
Tasks are simple classes that contain methods which can have parameters that are handled by the mapping algorithm:
@Named
public class MyTask {
@Inject
private ModelService modelService;
public void doSomething(int id, String name, Object value) {
Model model = modelService.get(id);
model.setProperty(name, value);
model.save();
}
}
Example 4.11. A task class
Execute such a task (called mytasks) via the TaskQueue as follows:
@Inject
private TaskQueueService taskQueueService;
public void executeInTaskQueue() {
taskQueueService.queue("mytasks", MyTask.class).doSomething(4711, "hello", "world");
}
Example 4.12. Execute a task