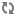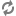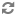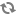To connect your applications with Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) providers such as Facebook and Twitter, Elastic Social provides a library for integration of Spring Social, which is an extension of the Spring Framework. Please refer to the Spring Social Documentation for an explanation of concepts and integration details.
To use this library along with the Facebook and Twitter connectors you have to add the following dependencies to your POM:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
...
<dependencies>
...
<dependency>
<groupId>com.coremedia.elastic.social</groupId>
<artifactId>social-spring-social</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.social</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-social-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.social</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-social-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.social</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-social-facebook</artifactId>
<version>2.0.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.social</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-social-twitter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
...
</dependencies>
...
</project>
Example 4.25. Dependencies for Facebook and Twitter integration
Elastic Social includes implementations of the
ConnectionRepository and UsersConnectionRepository interfaces
which use the CommunityUserService to store and retrieve the provider connection
information. Furthermore, a special SignInAdapter is provided which checks if a user may sign in and sets the
Spring Security context accordingly. See the API Documentation of the
com.coremedia.elastic.social.springsocial package for details.
The following example shows a Spring Java @Configuration class which configures the
Elastic Social classes for Spring Social. This configuration takes into account
that a multi-tenant application may require different service provider credentials for each tenant. This is
accomplished through a special Spring scope called tenant which is provided by the core-impl module of Elastic
Social.
import com.coremedia.elastic.core.api.settings.Settings;
import com.coremedia.elastic.core.api.tenant.TenantService;
import com.coremedia.elastic.social.springsocial. \
CommunityUserSignInAdapter;
import com.coremedia.elastic.social.springsocial. \
CommunityUsersConnectionRepository;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ScopedProxyMode;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.context. \
SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.social.connect.ConnectionFactoryLocator;
import org.springframework.social.connect.ConnectionRepository;
import org.springframework.social.connect.UsersConnectionRepository;
import org.springframework.social.connect.support. \
ConnectionFactoryRegistry;
import org.springframework.social.connect.web.ConnectController;
import org.springframework.social.connect.web. \
ProviderSignInController;
import org.springframework.social.connect.web.SignInAdapter;
import org.springframework.social.facebook.connect. \
FacebookConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.social.twitter.connect. \
TwitterConnectionFactory;
import javax.inject.Inject;
@Configuration
public class SpringSocialConfiguration {
@Inject
private TenantService tenantService;
@Inject
private Settings settings;
@Bean
@Scope(value = "tenant", proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.INTERFACES)
public ConnectionFactoryLocator connectionFactoryLocator() {
ConnectionFactoryRegistry registry =
new ConnectionFactoryRegistry();
String tenant = tenantService.getCurrent();
// you need to add methods to get the Facebook and Twitter connection settings
registry.addConnectionFactory(new FacebookConnectionFactory(
getFacebookClientId(), getFacebookClientSecret()
));
registry.addConnectionFactory(new TwitterConnectionFactory(
getTwitterConsumerKey(), getTwitterConsumerSecret()
));
return registry;
}
@Bean
@Scope(value = "request", proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.INTERFACES)
public ConnectionRepository connectionRepository() {
Authentication authentication =
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (authentication == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to get a
ConnectionRepository: no user signed in");
}
return usersConnectionRepository().\
createConnectionRepository(authentication.getName());
}
@Bean
public UsersConnectionRepository usersConnectionRepository() {
return new CommunityUsersConnectionRepository();
}
@Bean
public SignInAdapter signInAdapter() {
return new CommunityUserSignInAdapter();
}
@Bean
public ProviderSignInController providerSignInController() {
return new ProviderSignInController(
connectionFactoryLocator(),
usersConnectionRepository(), signInAdapter());
}
@Bean
public ConnectController connectController() {
return new ConnectController(
connectionFactoryLocator(), connectionRepository());
}
...
}
Example 4.26. Configuring Elastic Social classes for Spring Social