Connector for HCL Commerce Manual / Version 2506.0
Table Of ContentsThe CoreMedia system uses caching to speed-up access to various eCommerce entities (e.g. catalogs, categories, products, segments etc.). These entities are cached when they are requested by the CoreMedia system.
Commerce-Hub Cache Infrastructure
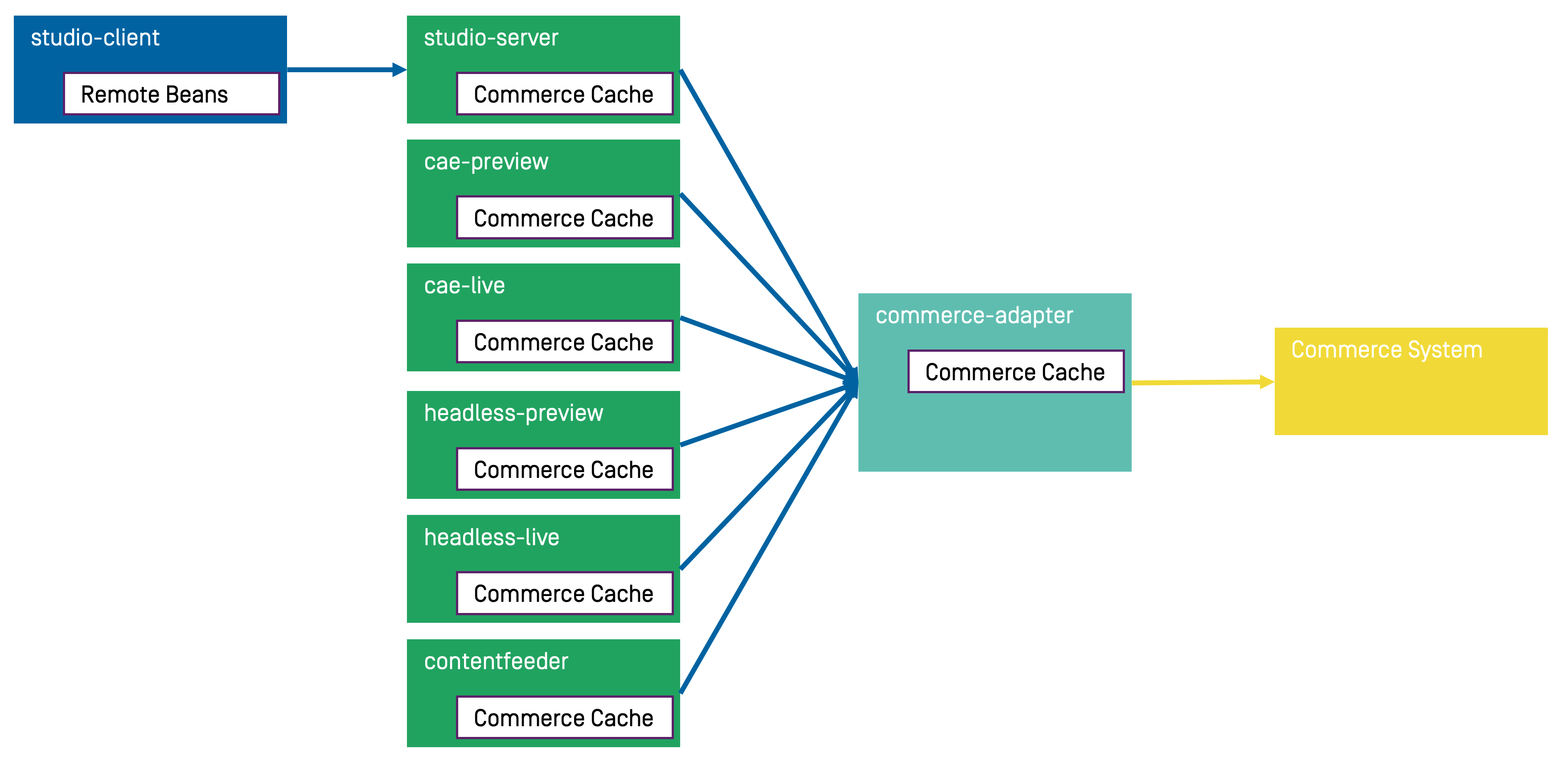
Caching of commerce entities is implemented in different layers of the Commerce Hub infrastructure:
Caching is implemented in the Commerce Adapter to accelerate access to commerce entities and to avoid heavy traffic on the HCL Commerce system due to multiple clients connected to the same system.
Caching is implemented in the Commerce Adapter client library which is used in Studio, Content Application Engine, Headless Server and Content Feeder. This avoids redundant network communication with the Commerce Adapter when accessing commerce entities.
Caching is implemented in the Studio Client. Commerce entities are loaded as
RemoteBeansand take part in the Studio invalidation mechanism. Updates can be displayed directly if they are recognized.
Java based apps like the Commerce Adapter and Commerce Adapter clients, e.g., Studio, Content Application Engine, Headless Server, and Content Feeder, use the CoreMedia Cache to cache commerce entities.

Note
It is recommended to cache as many commerce entities as possible in the Commerce Adapter for a rather long time and to enable both immediate recomputation and persistent caching of messages as described further down in this chapter. Commerce client apps may then be configured to use rather small caching times and small capacities for commerce entities.
Cache Invalidation by Actuator
Commerce entities are cached for a configurable time span. Changes made to commerce items on the HCL Commerce won't be visible until this cache time expires. Two issues arise when only relying on the expiry of cache keys.
First, a proper adjustment of the cache times compromises between two requirements: On the one hand cache times should be short in order to provide an up-to-date system. On the other hand cache times should be long in order to reduce the traffic on the HCL Commerce. Second, updating a cache entry requires a controlled invalidation across all relevant caches of the Commerce Hub infrastructure. It is not sufficient to have a cache entry expire in one cache if other caches are still returning the old value.
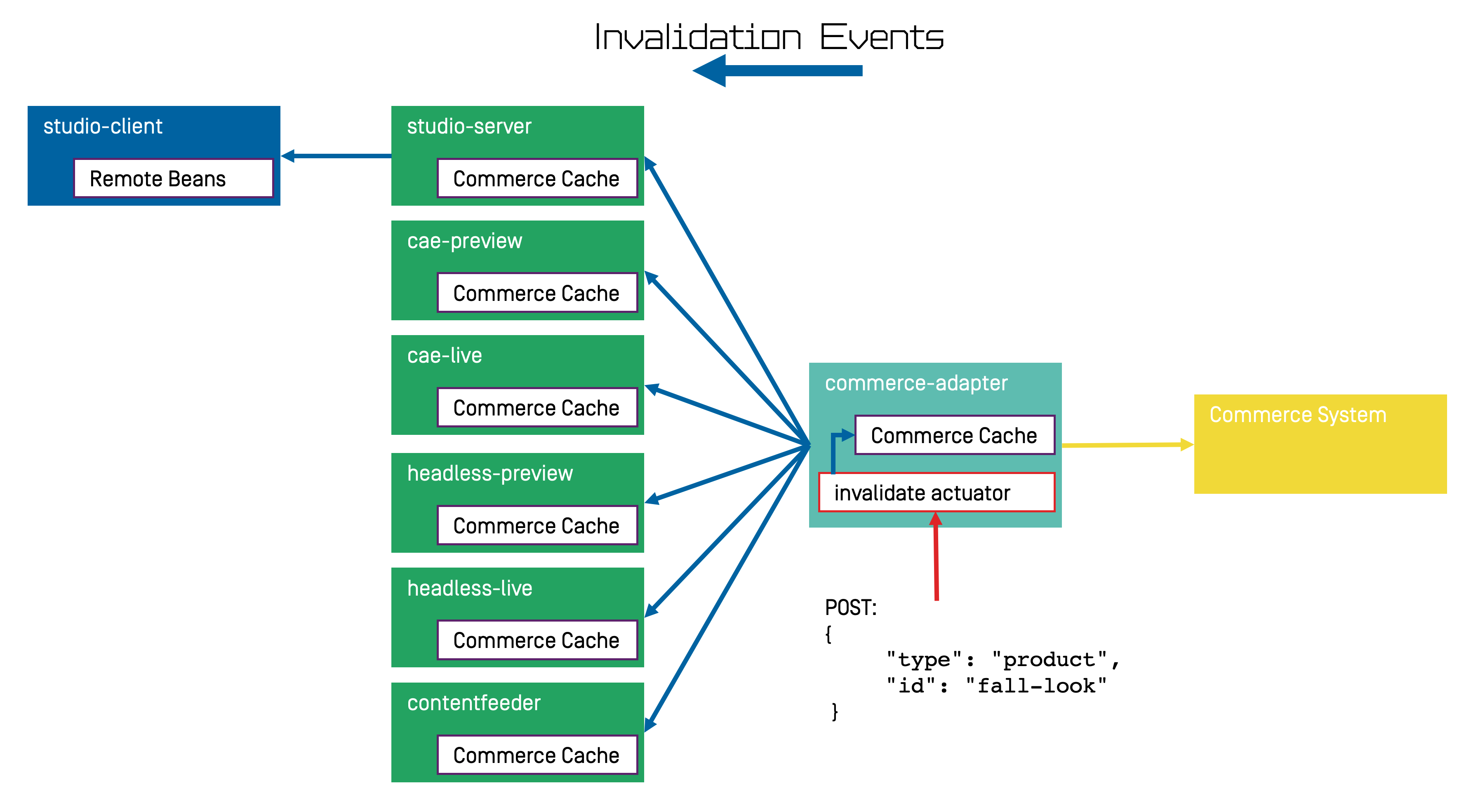
The Commerce Adapter is the central component that addresses both issues.
It allows for a proactive invalidation of cache entries via the invalidate actuator
and it informs all connected caches about this invalidation.
Each client connects as an invalidation observer to the adapter and is notified when
a cache entry is to be invalidated.
The propagation of the
invalidation event ensures that all connected client caches are also updated.
The actuator can be triggered manually or via custom scripts depending on the workflow of the connected
HCL Commerce. If the update cycles of the HCL Commerce are known or if changes can be detected
automatically and be used to trigger a script invoking the invalidate actuator, then
long cache times can be configured to hold commerce entities in the cache as long as possible.
The following figure shows the actuator component in the Commerce Adapter and the direction of events propagating the invalidation.
The actuator can be called by using a POST request.
http://<adapter-host>:<adapter-port>/actuator/invalidate
The body is of JSON code with 2 mandatory parameters;
all must be present but can also be left empty.
type-
The entity type. Can be one of the following values:
catalog,category,product,segment,marketing_spot. Further values can be registered in a project customization. If it is empty, the value remains unspecified and, for example, all items with the giventypeare invalidated. id- The entity ID. If it is empty, all items of an entity type are invalidated.
Examples:
{ "type": "product", "id": "dress-3" }-
Invalidate product
dress-3in the Commerce Adapter and in all connected clients. { "type": "category", "id": "dresses" }-
Invalidate category
dressesin the Commerce Adapter and in all connected clients. { "type": "category", "id": "" }- Invalidate all categories in the Commerce Adapter and in all connected clients.
{ "type": "", "id": "" }- Invalidate all commerce items in the Commerce Adapter and in all connected clients (invalidate all).

Note
If a client misses a notification, for example because it is unavailable, it would continue to deliver the old value until the next invalidation comes in, either via actuator or timeout. If there is any suspicion that a cache is out-of-sync, the actuator can be called again.
Invalidation messages from Commerce Adapter to the connected clients can also be turned off using the following configuration property. Then the cache items in the clients disappear only after they have expired. Invalidation messages are turned on by default.
entities.send-invalidations=true

Note
Please note, there is no automatic mechanism involved that is able to trigger the invalidation when a commerce item is changed in the HCL Commerce. Such a mechanism can be provided in projects.
Immediate Recomputation of Cache Keys
Commerce entities can be recomputed immediately if they are invalidated in the Commerce Adapter using the following configuration property. This feature is useful to keep the cache of the Commerce Adapter filled with the most frequently used commerce entities. The feature is turned off by default.
entities.recompute-on-invalidation=true

Note
Recomputation is triggered no matter if the invalidation was send from the cache timer or
the invalidate actuator.
Cache keys that are evicted due to space considerations of the cache are not recomputed.
Persisted Caching of gRPC Messages
Incoming and outgoing gRPC messages can be saved to disk to speed-up the Commerce Adapter. This feature allows the Commerce Adapter to read messages from disk when started and to use the restored messages for the following two purposes:
Immediately respond to requests with the restored response.
Replay the restored requests so that the cache fills with up-to-date values served by the HCL Commerce.
When all requests have been replayed the restored messages are discarded so that responses are
only taken from the commerce cache. New incoming requests and their responses are saved to disk
using the allowed maximum number of files configured via entities.message-store.files.
The allowed number of files default to the configured cache capacities as described in the next section.
The feature is turned off by default but can be enabled by setting the following configuration property
so that it points to an existing directory.
entities.message-store.root=file://<PATH_TO_DIRECTORY>

Warning
The directory configured via entities.message-store.root must not be a shared directory.

Note
The contents of the directory configured via entities.message-store.root
may be copied so that new Commerce Adapter instances read messages written by another Commerce Adapter.
Cache Configuration of the Commerce Adapter

Note
This chapter applies to the Commerce Adapter, but not to the generic clients like Studio, Content Application Engine, Headless Server and Content Feeder.
In order to adjust the cache configuration you can use the following properties for cache capacities and cache timeouts respectively:
cache.capacities.*cache.timeout-seconds.*
The last part of the configuration property is the config key. Each cache key, e.g. for a product, is using its
well known config key (e.g. product) to set the capacity and the cache time.
The cache capacity denotes the number of commerce entities that the cache can hold of a specific cache class
while the cache time specifies the duration that the cache can hold a commerce entity.
There are 2 types of config keys, those that are the same for all different commerce adapters and those that
are specific to each vendor adapter. A wide part of the caching is already done within the base adapter
library on Service level (e.g. the ProductService) and does not have
to be done in each vendor specific adapter.
Common base adapter config keys:
- catalogs
The list of all catalogs for a store referenced by ID and the definition of the default catalog.
- catalog
A catalog with its properties and a reference to the root category.
- category
A category with its properties. Sub-categories are referenced by ID, as well as products that belong directly to the category. Probably all categories should be cached. They are often used and often traversed. The memory consumption of each cache entry should be small, but can increase if custom attributes are used.
- product
Products and variants/SKUs altogether. Please note, there is no distinction between base products and variants/SKUs. Keep this in mind when choosing a capacity value! The memory consumption of each cache entry should be small, but can increase if custom attributes are used.
- segments
The list of all customer segments referenced by ID.
- segment
A customer segment with its properties. The memory consumption of each cache entry is very small.
- marketingspots
The list of all marketing spots referenced by ID.
- marketingspot
A marketing spot with its properties. The memory consumption of each cache entry is very small.
Vendor specific config keys:
- previewtoken
Preview tokens to support the Studio preview of commerce pages. A new token is requested for each new combination of preview parameters (e.g. customer segments, preview date). The cache time should be less than the default expiration time in the commerce system.
- storeinfo
The global store info with all available catalogs referenced by name and ID.
- categoryid
Used to map tech IDs to external IDs of categories. The memory consumption of each cache entry is very small.
- categorydata
Used to build storefront URLs and in services that are not already cached in the base adapter (e.g.
PriceService,LinkService,CartService). Each entry consumes ~10kB heap memory.- productid
Used to map tech IDs to external IDs of products and variants/SKUs. The memory consumption of each cache entry is very small.
- productdata
Used to build storefront URLs and in services that are not already cached in the base adapter (e.g.
PriceService,LinkService,CartService). Please note, there is no distinction between base products and variants/SKUs. Keep this in mind when choosing a capacity value! Each entry consumes ~100kB heap memory.- dynamicprice
To retrieve personalized prices for products and SKUs. Please note, there is no distinction between base products and variants/SKUs. Keep this in mind when choosing a capacity value! The memory consumption of each cache entry is small.
- staticprice
To retrieve static list prices for products and SKUs. Please note, there is no distinction between base products and variants/SKUs. Keep this in mind when choosing a capacity value! The memory consumption of each cache entry is small.
The default values for the capacity and cache time of each cache key can be found in the in the
application.properties file in the adapter or consult the Spring Boot environment
actuator of the app.
Commerce Cache Configuration of Commerce Adapter Clients

Note
This chapter applies to Commerce Adapter clients like Studio, Content Application Engine, Headless Server and Content Feeder.
Every commerce cache class has a default capacity and default cache time configured in the application. Each of the default values can be adapted to the needs of your system environment by overwriting the corresponding properties.
Refer to the Chapter 12, Commerce Adapter Properties if you want to adjust the cache configuration for your Commerce Adapter
In order to adjust the cache configuration you can use the following properties (see Section 3.7, “Commerce Hub Properties” in Deployment Manual for details) for cache capacities and cache timeouts respectively:
cache.capacities.ecommerce.*cache.timeout-seconds.ecommerce.*
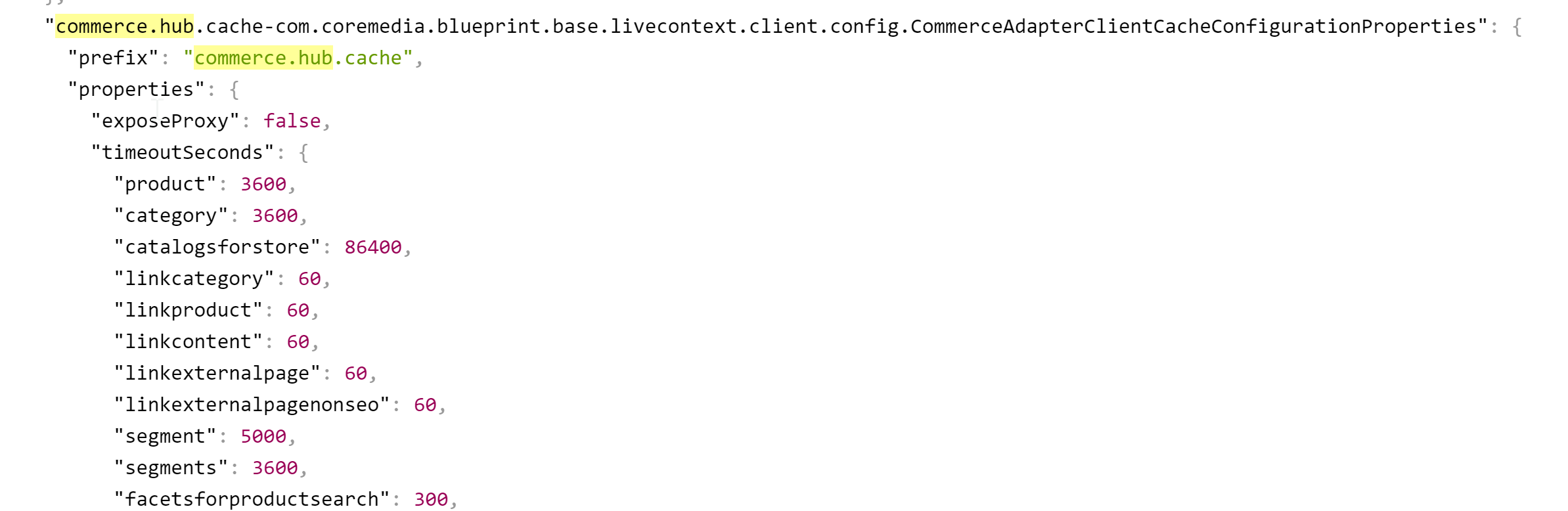
You have to replace the trailing "*" with the configuration key of the concrete cache key. You can find the keys and
the default values using the Actuator URLs from the default overview page (https://overview.docker.localhost)
in the default Blueprint Docker deployment. Click the Config link and search for the
cache.capacities.ecommerce or cache.timeout-seconds.ecommerce prefix.