Personalization Hub Manual / Version 2506.0
Table Of Contents
The adapter depends on core features that must be enabled by setting the
Spring property cmec.enabled to true
for CoreMedia Studio Server, Content Application Engine, and Headless Server.
Additionally, parameters for connecting to CoreMedia Engagement Cloud are needed. This configuration can be provided in either settings content items or as Spring configuration properties. Settings content items take precedence over Spring configuration properties. The following settings content items are considered in descending order of priority:
Settings content items linked from the root channel of the site that forms the context of the request.
The settings are site-specific because different sites might require a different configuration, especially with respect to the region in CoreMedia Engagement Cloud to which they are associated. Multiple sites can be connected to the same region. In those cases the settings document may be created outside the sites and linked to multiple sites.
The settings content items at the path
Options/Settings/Internal/Engagement Cloudbelow the site root folder of the site that forms the context of the request. If needed, this path can be adjusted using the Spring propertycmec.site-configuration-path.Because such settings content items are located by path, they do not have to be published with the site root channel. This allows you to keep certain settings in the management environment, only, for example, the password needed to access the CoreMedia Engagement Cloud API.
The settings content item at the path
/Settings/Options/Settings/Internal/Engagement Cloud. This allows you to provide default settings for all sites without linking the settings in all sites. If needed, this path can be adjusted using the Spring propertycmec.global-configuration-path.
In each settings content item the configuration is expected in a substruct
engagement. As usual, we strongly recommend to store credentials securely.
If passwords are stored in the Content Repository, they must be encrypted,
but it is preferable to inject them through Spring configuration properties.
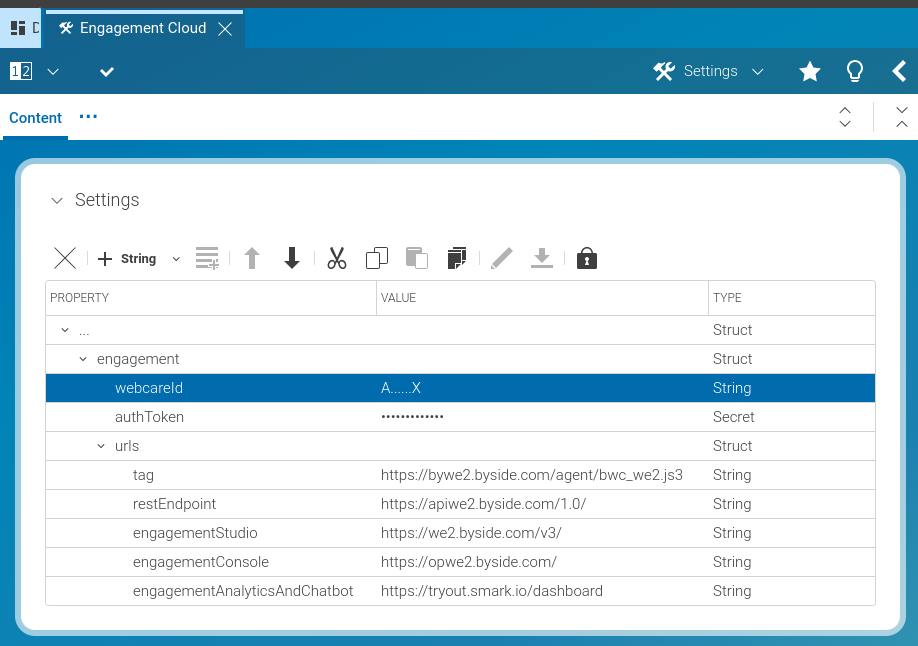
The following figure shows the settings content item structure when edited in CoreMedia Studio.
| Setting | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| webcareId |
The webcare id of the CoreMedia Engagement Cloud account the site is connecting to. | |
| password |
The password associated with the webcare id. | |
| region | we1 |
The CoreMedia Engagement Cloud region in which the webcare id of a site is located.
One of: |
| urls.tag |
https://cdn.engagement.coremedia.cloud/cmec/we2.js |
The region specific URL of the CoreMedia Engagement Cloud tag. |
Table 4.1. CoreMedia Engagement Cloud properties in settings content items
In case the settings content items do not contain a certain property, Spring configuration properties are used instead. See Section 3.19, “Engagement Cloud Integration Properties” in Deployment Manual for the available properties, which allow you to define webcare id, region, and password per site or as global defaults.

Note
When embedding the JavaScript library of CoreMedia Engagement Cloud by the CAE,
only the settings content items linked from the root channel of the site
are considered for reading webcareId and urls.tag.
Other settings content items and Spring configuration options are ignored
in this specific case.
Additionally, a mapping between CoreMedia Content Cloud groups and CoreMedia Engagement Cloud groups can be configured using Spring properties. When navigating from CoreMedia Studio to CoreMedia Engagement Cloud a user with appropriate CoreMedia Engagement Cloud groups is automatically created. See Section 3.19, “Engagement Cloud Integration Properties” in Deployment Manual for details about the mapping.
The Deployment Manual also provides a description of additional properties for configuring connection timeouts and properties to adjust the expected locations of settings content items.