Studio Developer Manual / Version 2506.0
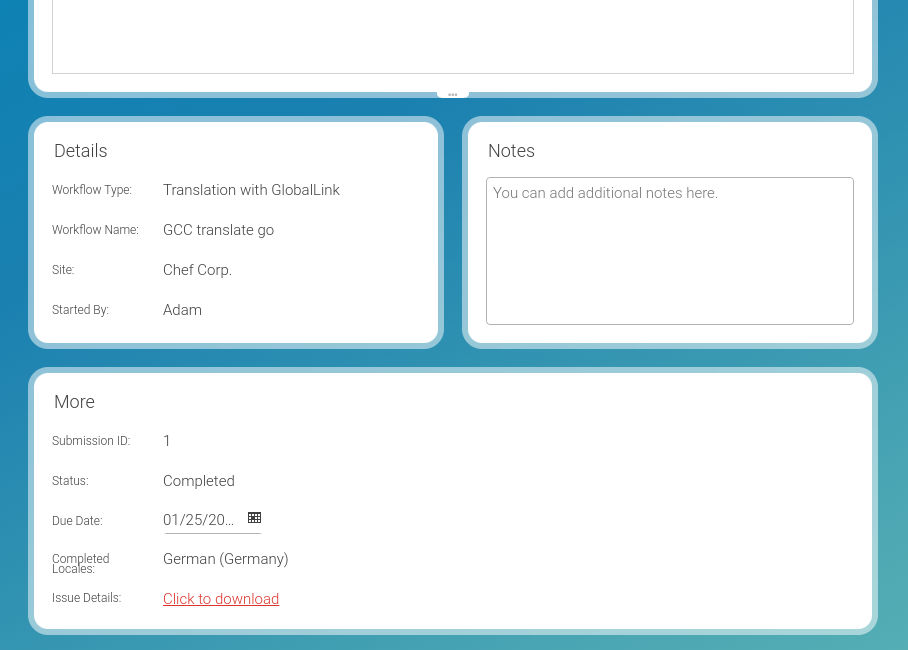
Table Of ContentsThe Global Link Translation Workflow defines several extra fields for a running workflow form as shown in figure Figure 9.12, “Running Workflow form Extension for a Running Global Link Translation Workflow” (note that the "Due Date" field is an input field here for the sake of the example, it is normally a read-only field for a running Global Link workflow).
The following code gives the complete definition of the running workflow form extension for the the Global Link Translation Workflow. The details are explained afterward.
import { workflowPlugins } from "@coremedia/studio-client.workflow-plugin-models/WorkflowPluginRegistry";
import { Binding, DateTimeField } from "@coremedia/studio-client.workflow-plugin-models/CustomWorkflowApi";
import { getLocalizer } from "@coremedia/studio-client.i18n-models";
import Gcc_properties from "./Gcc_properties";
interface GccViewModel {
globalLinkPdSubmissionIds?: string;
globalLinkSubmissionStatus?: string;
submissionStatusHidden?: boolean;
globalLinkDueDate?: Date;
globalLinkDueCalendar?: Calendar;
globalLinkDueDateText?: string;
completedLocales?: string;
completedLocalesTooltip?: string;
xliffResultDownloadNotAvailable?: boolean;
}
const getGccWorkflowPlugin = async (): Promise<TranslationWorkflowPlugin> => {
const localizer = await getLocalizer(Gcc_properties);
return {
workflowName: "TranslationGlobalLink",
nextStepVariable: "translationAction",
startWorkflowFormExtension: {...},
runningWorkflowFormExtension: StartWorkflowFormExtension<GccViewModel>({
computeTaskFromProcess: (process) => process.getCurrentTask(),
computeViewModel(state: WorkflowState): GccViewModel {
return {
globalLinkPdSubmissionIds:
transformSubmissionId(state.process.getProperties()
.get("globalLinkPdSubmissionIds")),
globalLinkSubmissionStatus:
transformSubmissionStatus(state.process.getProperties()
.get("globalLinkSubmissionStatus")),
globalLinkDueDate:
dateToDate(state.process.getProperties().get("globalLinkDueDate")),
completedLocales:
convertLocales(state.process.getProperties().get("completedLocales")),
completedLocalesTooltip:
createQuickTipText(state.process.getProperties()
.get("completedLocales"), localesService),
xliffResultDownloadNotAvailable:
downloadNotAvailable(state.task),
};
},
saveViewModel(viewModel: GccViewModel) {
return {
globalLinkDueDate: viewModel.globalLinkDueDate,
}
},
fields: [
TextField({
label: localizer("TranslationGlobalLink_submission_id_key"),
value: Binding("globalLinkPdSubmissionIds"),
readonly: true,
}),
TextField({
label: localizer("TranslationGlobalLink_submission_status_key"),
value: Binding("globalLinkSubmissionStatus"),
readonly: true,
}),
DateField({
label: localizer("TranslationGlobalLink_submission_dueDate_key"),
value: Binding("globalLinkDueDate")
}),
TextField({
label: localizer("TranslationGlobalLink_completed_Locales"),
readonly: true,
value: Binding("completedLocales"),
tooltip: Binding("completedLocalesTooltip"),
}),
Button({
label: localizer("translationResultXliff_Label_Button_text"),
value: localizer("Gcc_properties.translationResultXliff_Button_text"),
validationState: "error",
handler: (state): GccViewModel | void => downloadXliff(state.task),
hidden: Binding("xliffResultDownloadNotAvailable"),
}),
]
}),
...
};
};
getGccWorkflowPlugin().then((gccWorkflowPlugin) => {
workflowPlugins._.addTranslationWorkflowPlugin(gccWorkflowPlugin);
});
Example 9.112. Running workflow form extension for Global Link Translation Workflow
To customize the running workflow form for a custom workflow, the parameter WorkflowPlugin#runningWorkflowFormExtension<M extends ViewModel> is used.
The view model is the same as for the startWorkflowFormExtension. It is created with the factory function RunningWorkflowFormExtension<M extends ViewModel>()
which has very similar parameters to those of the previous section:
- computeTaskFromProcess?: (process: Process) => Task | null | undefined;
An optional function to compute the current task from a given process. Its purpose is described under the following point.
- computeViewModel(state: WorkflowState): M
A function that computes the view model for the extension's fields. Contrary to the
StartWorkflowFormExtension#computeViewModel()function it receives aWorkflowStateparameter. It has the two propertiesWorkflowState#process(aProcessremote bean) andWorkflowState#task(aTaskremote bean) which hold the currently displayed process and task respectively.Note that the
processproperty is always given and that the bean is fully loaded. For thetaskproperty, things are a bit more complicated. It is set if either (1) the workflow form displays a task (e.g., opened from "Inbox") or (2) the workflow form displays a process (e.g., opened from "Running") butRunningWorkflowFormExtension#computeTaskFromProcess()from above is given. Otherwisetaskis set tonull.Note that the function
computeTaskFromProcessis wrapped in a dependency-trackedFunctionValueExpressionunder the hood. Thus, it may returnundefinedas long as the current task cannot be computed due to asynchronous sub-computations. The surrounding framework ensures thatRunningWorkflowFormExtension#computeViewModel(state: WorkflowState)will always be called with aWorkflowStateparameter where theprocessandtaskremote bean properties are set and fully loaded (with the one exception from above wheretaskisnull).In the example, several view model properties are computed based on the current
WorkflowState. While some computations are just access calls to the process variables, others require more complex computations and utilize helper functions.- saveViewModel(viewModel: M): Record<string, unknown>
Contrary to
StartWorkflowFormExtension#saveViewModel()function, this function to save the view model changes back to the process is not only called once (upon workflow start) but whenever the view model changes.- fields
An array of the running form extension's fields. The same explanations as for
StartWorkflowFormExtension#fieldsapply here. The example shows a mixture of field properties that are directly set or bound to a view model property.- remotelyValidatedViewModelFields?: (keyof M)[]
The same explanations as for
StartWorkflowFormExtension#remotelyValidatedViewModelFieldsapply here.- viewModelValidator?: (viewModel: M) => WorkflowSetIssues
The same explanations as for
StartWorkflowFormExtension#viewModelValidatorapply here.