Studio Developer Manual / Version 2104
Table Of Contents
In order to hide components on a content form, the service HideService is used.
This service deals only with Studio components which implements IHidableMixin:
package com.coremedia.ui.mixins {
import ext.IMixin;
/**
* Adds hide properties feature to the component this mixin is mixed into.
*
*/
[Mixin("com.coremedia.ui.mixins.HidableMixin")]
public interface IHidableMixin extends IMixin {
/**
* Sets the text used to display this component in the hide service dialog.
*/
[Bindable]
function set hideText(newHideText:String):void;
/**
* @return the text used to display this component in the hide service dialog.
*/
[Bindable]
function get hideText():String;
/**
* Sets the optional id to identify this component.
* If not available the mixin demands the presence of the component's item id
* The id might be used to persist the state of this component and
* should be hence permanent.
*/
[Bindable]
function set hideId(newHideId:String):void;
/**
* Gets the optional id to identify this component.
* The id might be used to persist the state of this component and
* should be hence permanent.
*/
[Bindable]
function get hideId():String;
}
}
Example 7.36. IHidableMixin.as
Any Studio component not implementing this mixin will be ignored by the HideService service.
In the standard Blueprint Studio all relevant fields on the content forms already implement the mixin.
Your customized fields, though, must implement the mixin so that they are considered by HideService.
- hideId
An ID which must be global for a given content type. Usually you don't have to set it for yourself. But it is internally set to
propertyNamewhen the given component is a property field. See Section 7.4, “Customizing Property Fields” for details about property fields.For the HideService to persist the hidden state of a component the component itself and its parent up to the
DocumentFormmust have anitemIdor ahideId.- hideText
The text is used to display the corresponding component in the hide service dialog. For example, for a
FieldContainerit is recommended to set it to the function callgetFieldLabel().
Blueprint example code of hideable components
Have a look at an Blueprint example of the requirements.
The first level children of a content form are all of the type DocumentForm which implements the mixin
in its base class.
The following code of DocumentFormBase.as shows the implementation of the mixin.
package com.coremedia.cms.editor.sdk.premular {
import com.coremedia.ui.components.FloatingToolbarContainer;
import com.coremedia.ui.mixins.IHidableMixin;
public class DocumentFormBase extends FloatingToolbarContainer implements IHidableMixin{
// The title of this form when used as a tab.
[Bindable]
public var title:String;
public function DocumentFormBase(config:DocumentForm = null) {
super(config);
}
/** @private */
/** @inheritDoc */
[Bindable]
public native function set hideId(newHideId:String):void;
/** @inheritDoc */
[Bindable]
public native function get hideId():String;
/** @private */
[Bindable]
public function set hideText(newHideText:String):void {
// The hideText is determined by the getter. Nothing to do.
}
/** @inheritDoc */
[Bindable]
public function get hideText():String {
return title;
}
}
}
Example 7.37. DocumentFormBase.as
The document form uses the title property for the tab label, therefore, the mixin implementation of
hideText uses the same as well.
Note that the setter of hideText has an empty block as you can change the hideText only by
changing the title.
Take a look into the code snippet of CMArticleForm.mxml which renders the content form for the content type
CMArticle:
<editor:items>
<editor:DocumentForm
title="{resourceManager.getString('com.coremedia.blueprint.studio.BlueprintTabs', 'Tab_content_title')}"
itemId="contentTab">
<editor:items>
<bpforms:DetailsDocumentForm bindTo="{config.bindTo}"/>
<bpforms:TeaserDocumentForm bindTo="{config.bindTo}"
collapsed="true"/>
<bpforms:MediaDocumentForm bindTo="{config.bindTo}"/>
<bpforms:AuthorLinkListDocumentForm bindTo="{config.bindTo}"/>
<bpforms:RelatedDocumentForm bindTo="{config.bindTo}"/>
<bpforms:ViewTypeSelectorForm bindTo="{config.bindTo}"/>
<bpforms:ExternallyVisibleDateForm bindTo="{config.bindTo}"/>
<bpforms:ValidityDocumentForm bindTo="{config.bindTo}"/>
</editor:items>
</editor:DocumentForm>
<bpforms:DefaultExtraDataForm/>
<bpforms:MultiLanguageDocumentForm bindTo="{config.bindTo}"/>
<bpforms:CMArticleSystemForm bindTo="{config.bindTo}"/>
</editor:items>
Example 7.38. CMArticleForm.mxml
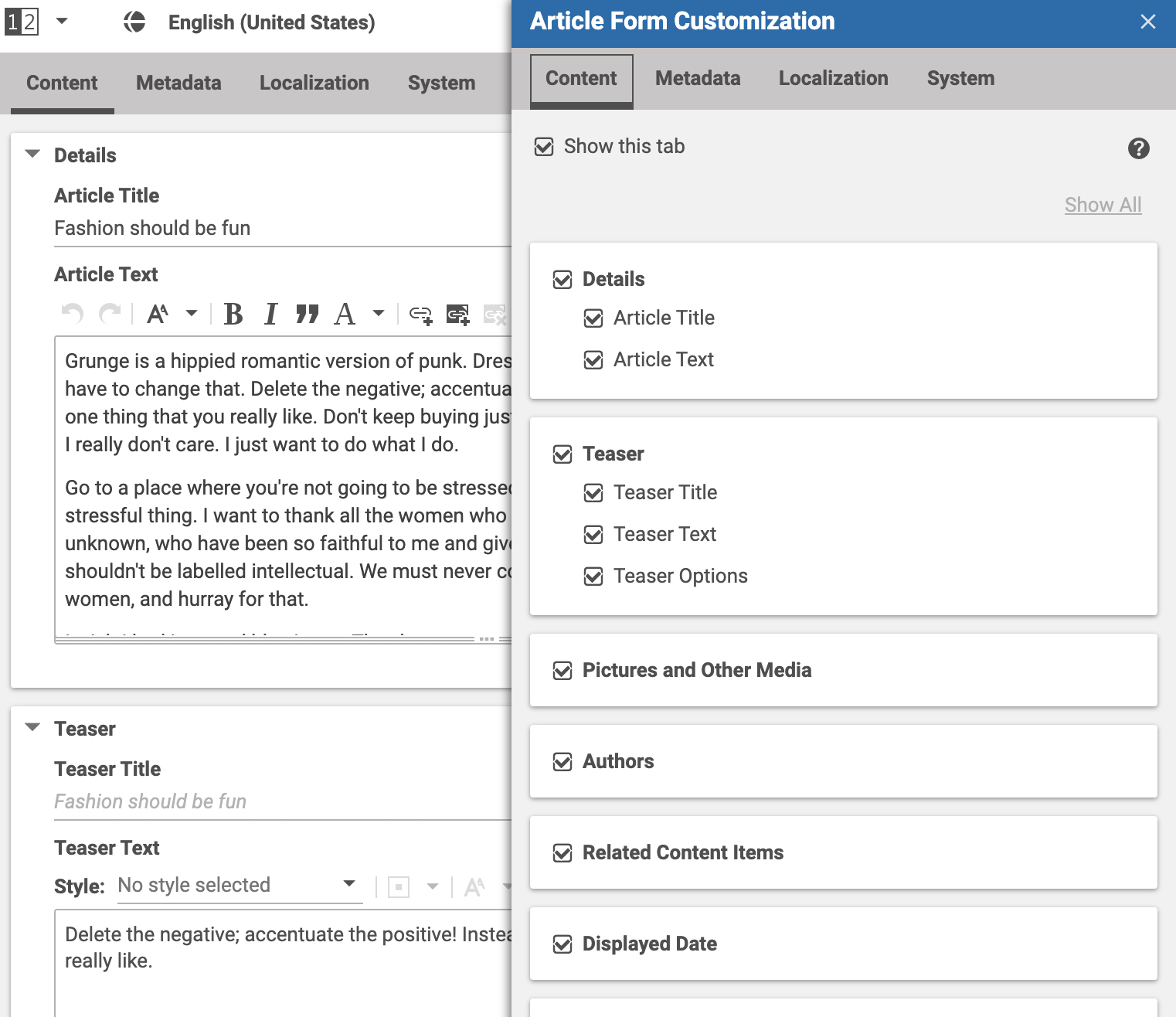
The code shows four children of the type DocumentForm which represent the four tabs of the content form
as seen in the following screenshot:
You can see that the first document form has the itemId "ContentTab".
The other document forms DefaultExtraDataForm, MultiLanguageDocumentForm and
CMArticleSystemForm have all their own itemId defined in the respective MXML files.
The first child on the "Content" document tab is the property field group "Details" with sub children "Article Title"
and "Article Text". The fields are defined in DetailsDocumentForm.mxml which is a subtype of
CollapsiblePanel which also implements the IHidableMixin:
<editor:items>
<editor:StringPropertyField itemId="title" propertyName="title"/>
<editor:RichTextPropertyField bindTo="{config.bindTo}"
itemId="detailText"
propertyName="detailText"
initialHeight="200"/>
</editor:items>
Example 7.39. DetailsDocumentForm.mxml
Again, each item has its own itemId.
In addition both StringPropertyField and RichTextPropertyField are the subtype of
AdvancedFieldContainer which implements the IHidableMixin.