Requirements
Most websites define business rules that require content to be classified into certain categories. Typical examples include use cases such as "Display the latest articles that have been labeled as press releases" or "Promote content tagged with 'Travel' and 'London' to visitors of pages tagged with 'Olympic Games 2012'" etc.
Keywords or tags are common means to categorize content. Employing a controlled vocabulary of tags can be more efficient than allowing free-form keyword input as it helps to prevent ambiguity when tagging content. Furthermore, a system that supports the convenient management of tags in groups or hierarchies is required for full editorial control of the tags used within a site.
Solution
Blueprint currently uses tag information in various ways:
It is possible to use the taxonomies of a content item as conditions for dynamic lists of content (such as "5 latest articles tagged with 'London').
In CoreMedia Adaptive Personalization tags can be used to gather information about the topics a site visitor is interested in (see
TaxonomyInterceptor).In CoreMedia Adaptive Personalization tag information representing the interests of visitors can be used to define user segments, conditions for personalized selection rules and personalized searches.
It is possible to display related content for a content item based on content that shares a similar set of tags (see
CMTeasableImpl#getRelatedBySimilarTaxonomies).
In CoreMedia Blueprint tags are represented as
CMTaxonomy content items which represent a controlled vocabulary that is organized
in a tree structure. CoreMedia Blueprint defines two controlled
vocabularies: Subject and location taxonomies that can be associated with all types inheriting
CMLinkable.
Taxonomy Management
Subject taxonomies can be used to tag content with "flat" information about the content's topic
(such as Olympic Games 2012). They can also enrich assets with hierarchical categorization for
fine-grained drill down navigation (such as Hardware / Printers / Laser Printer). Subject
Taxonomies are represented by the content type CMTaxonomy which defines the
following properties:
value
| |
| Type |
String
|
| Description | Name of this taxonomy node |
children
| |
| Type |
Link list
|
| Description | References to subnodes of this taxonomy node |
externalReference
| |
| Type |
String
|
| Description | Reference of an equivalent entity in an external system in the form of an ID / URI etc. |
Table 6.6. CMTaxonomy Properties
Location taxonomies allow content to be associated with one or more locations. Location taxonomy
hierarchies can be used to retrieve content for a larger area even if it is only tagged with a
specific element within this area ("All articles for 'USA'" would include articles that are
tagged with the taxonomy node North America / USA / Louisiana / New Orleans). Location
taxonomies are represented by the content type CMLocTaxonomy which inherits from
CMTaxonomy and adds geographic information for more convenient editing and
visualization of a location.
latitudeLongitude
| |
| Type |
String
|
| Description | Latitude and longitude of this location separated by comma |
postcode
| |
| Type |
String
|
| Description | The post code of this location |
Table 6.7. Additional CMLocTaxonomy Properties
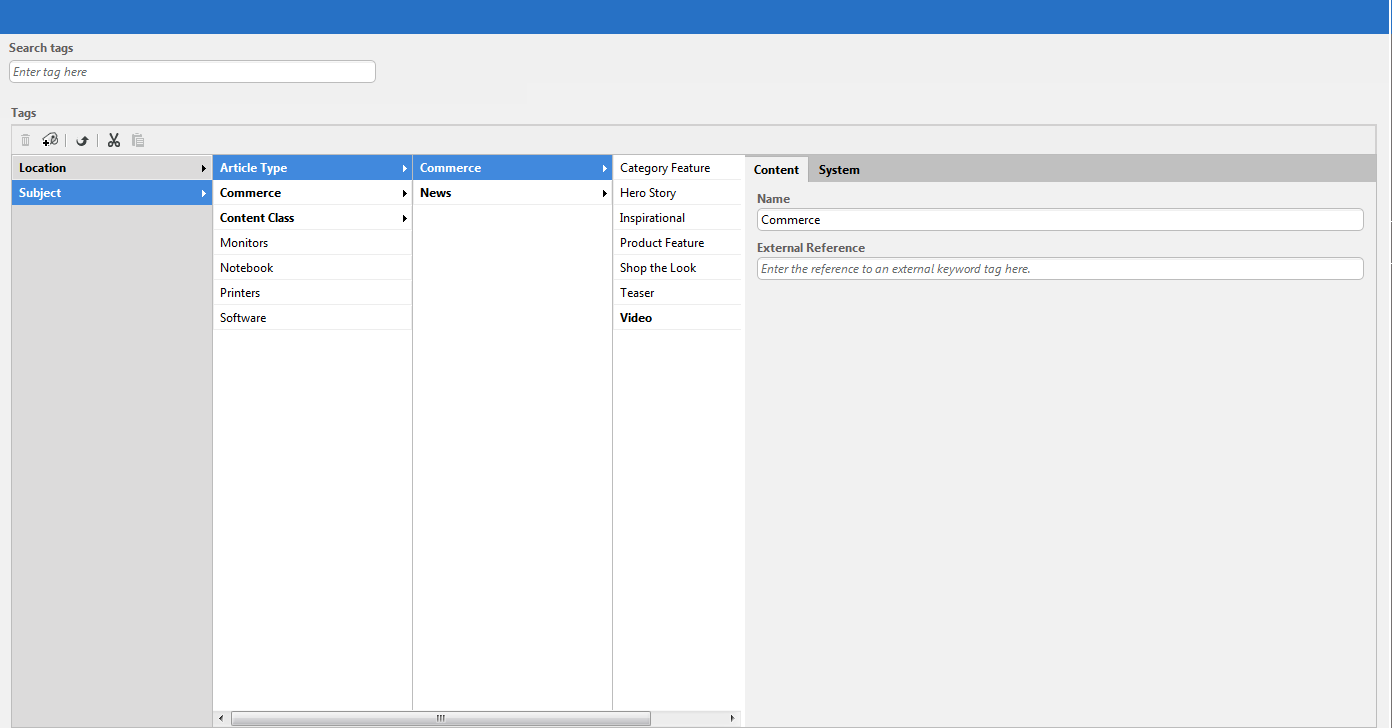
The taxonomy administration editor can be used to create a taxonomy and build a tree of keywords.
The taxonomy administration editor displays taxonomy trees and provides drag and drop support and the creation and deletion of keywords.
Taxonomy Assignment
To enable tagging of content two properties are available the CMLinkable content
type.
subjectTaxonomy
| |
| Type |
Link list
|
| Description | Subject(s) / topic(s) of that content item |
locationTaxonomy
| |
| Type |
Link list
|
| Description | Geographic location(s) of that content item |
Table 6.8. CMLinkable Properties for Tagging
| Property | Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
subjectTaxonomy
| Link list
| Subject(s) / topic(s) of that content item |
locationTaxonomy
| Link list
| Geographic location(s) of that content item |
Table 6.9. CMLinkable Properties for Tagging
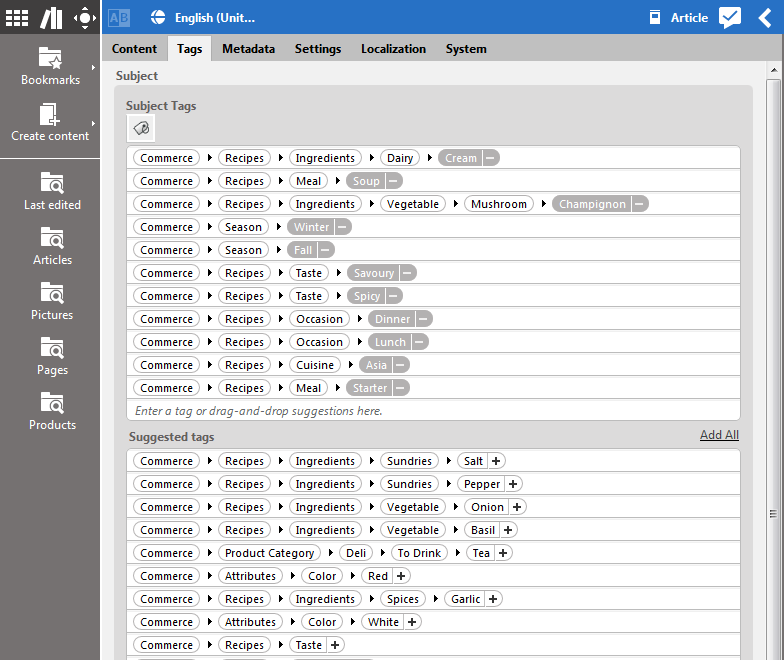
Editors can assign taxonomies to content items using CoreMedia Studio and the Blueprint taxonomy property editor. It allows for the following:
adding/removing references to taxonomy
autocompletion
suggestions
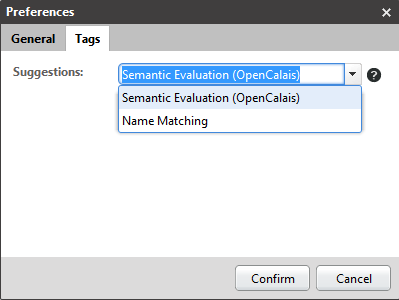
The user can add taxonomy keywords to the corresponding property link list using the taxonomy property editor. The editor also provides suggestions that are provided by the OpenCalais integration or a simple name matching algorithm. The strategy type can be configured in the preferences dialog of CoreMedia Studio.
How taxonomies are loaded
A Blueprint taxonomy tree is built through content items located in a specific folder of the content repository. As a default strategy for building a taxonomy tree, the taxonomy REST service of the taxonomy Studio extension looks up specific folders. Each document of the folder is analyzed for its position in the taxonomy tree. The name of the folder in which the taxonomy tree is placed defines the name of the taxonomy tree and is visible as a root node in the taxonomy administration UI. First level taxonomies must be placed directly within the root folder. Taxonomies of subsequent levels can also be placed in subfolders.
The lookup folders for taxonomies and the strategy used to build the tree are configured in the
Spring configuration file component-taxonomies.xml.
The bean property
<property name="taxonomyFolders" value="/Settings/Taxonomies/,Options/Taxonomies/"/>
configures the folders that are used to find taxonomies. Relative paths will be concatenated with the sites root folder.
The taxonomyFolders property is part of the
CMTaxonomyResolver class which actually detects the trees and wraps the
access to them through implementations of the interface Taxonomy.
CMTaxonomyResolver implements the interface
TaxonomyResolver so that it is possible to implement other taxonomy
detection strategies.
How to implement a new taxonomy resolver strategy
The CMTaxonomyResolver implements the interface
TaxonomyResolver and is injected to the
TaxonomyResource so that a request for a taxonomy is made in
CoreMedia Studio, the taxonomy resource instance looks up the
corresponding Taxonomy bean using the resolver instance. To change the
resolver strategy, inject another instance of TaxonomyResolver to the
TaxonomyResource.
How to implement a new taxonomy
If only the taxonomy build strategy will be changed, it is sufficient to keep the existing
CMTaxonomyStrategy. And only modify the instance creation of
CMTaxonomy and substitute it with an own implementation (for example a
folder based taxonomy strategy).
How to configure the document properties used for semantic strategies
The document properties that are used for a semantic evaluation are configured in the file
semantic-service.xml. The Spring configuration declares the abstract class
AbstractSemanticService that new semantic service can extend from. The
default properties used for a semantic suggestion search are:
titleteaserTitledetailTextteaserText
How to implement a new suggestion/semantic strategy
To add a new semantic strategy to Studio, it is necessary to implement the corresponding strategy for it and add it to CoreMedia Studio.
A new semantic strategy can easily be created by implementing the interface
SemanticStrategy. The result of a strategy is a Suggestions
instance with several Suggestion instances in it. Each
Suggestion instance must have a corresponding content instance in the
repository whose content type matches that one used for the taxonomy.
Blueprint uses CMTaxonomy documents for
keywords of a taxonomy, so suggestions must be fed with these documents. Additionally, a float
value weight can be set for each suggestion, describing how exactly the
keyword matches from 0 to 1. After implementing the semantic strategy, the implementing class
must be added to the Spring configuration, for example:
<customize:append id="semanticStrategyExamplesCustomizer" bean="semanticServiceStrategies" order="1000">
<list>
<ref bean="myMatching"/>
</list>
</customize:append>Next the new suggestion strategy has to be added to Studio, so that is selectable in CoreMedia Studio. For that proceed as follows:
Open the ActionScript file
TaxonomyPreferencesBase.asAdd a new key value for storing the strategy in the user preferences, for example
public static var TAXONOMY_MY_MATCHING_KEY:String = "myMatching";
Make sure that the constant value used here matched the Spring bean id of your suggestion strategy.
Add a new value to the taxonomy combo box in the preference dialog by adding the line
['Display name of My Suggestion Strategy', TAXONOMY_MY_MATCHING_KEY],
to method
getTaxonomyOptions(). This will add the display name with the corresponding combo box item value to the taxonomy combo box.Rebuild and restart Studio so that the changes take effect.
How to remove the OpenCalais suggestion strategy
If you want to disable the OpenCalais integration and remove the selection option from Studio, proceed as follows:
Remove the entry
<ref bean="semanticService"/>fromtaxonomies.xml.Remove the following line from the method
getTaxonomyOptionsof theTaxonomyPreferencesBase.asclass:[TaxonomyStudioPlugin_properties.INSTANCE. TaxonomyPreferences_value_semantic_opencalais_text, TAXONOMY_SEMANTIC_CALAIS_KEY]
In the same file as above, replace
DEFAULT_SUGGESTION_KEY:String = TAXONOMY_SEMANTIC_CALAIS_KEY;
with
DEFAULT_SUGGESTION_KEY = TAXONOMY_NAME_MATCHING_KEY;
How to add a site specific taxonomy
Adding a site specific taxonomy doesn't require any configuration effort. The logic how a site
depending taxonomy tree is looked up can be found in class
CMTaxonomyResolver.
To create a new site depending taxonomy proceed as follows:
Open Studio and select the folder
Options/Taxonomies/from the library.Create a new sub folder with the name of the new taxonomy.
The location for the new taxonomy has been created now.
To identify the type of taxonomy (such as
CMTaxonomyorCMLocTaxonomy) you have to create at least one taxonomy document in the new folder.
Once the taxonomy has been set up, additional nodes can be created using the taxonomy manager.
If the new taxonomy does not appear as new element in the column on the left, press the reload
button. It ensures that the CMTaxonomyResolver rebuilds the list of
available taxonomy trees. The new taxonomy is shown in the root column afterwards, include the
site name it is created in.
Creating site specific taxonomies allows you to overwrite existing ones. For example you create a
new taxonomy tree called Subject for site X and
open an article that is located in a sub folder of site X, the regular
Subject taxonomy property editor on the
Taxonomies tab in CoreMedia Studio will
access the Subject taxonomy of your new site, not the one that is located
in the global Settings folders. The suggestions and the chooser dialog
will also work in the new taxonomy tree.
How to configure the taxonomy property editor for a taxonomy
CoreMedia Blueprint comes with two types of taxonomies:
Subject and Location. The name of the taxonomy
matches the folder name they are located in, which is /Settings/Taxonomies.
When the taxonomy property editor for a Studio form is configured,
these IDs are passed to the property editor, for example
<taxonomy:taxonomyPropertyField propertyName="subjectTaxonomy"
taxonomyId="Subject"/>
<taxonomy:taxonomyPropertyField itemId="locTaxonomyItemId"
propertyName="locationTaxonomy"
taxonomyId="Location"/>As mentioned in the previous section, it is possible to overwrite the existing location or subject taxonomy with a site depending variant. In this case, it is not necessary to change the configuration for the property field. The taxonomy property editor will always try to identify the site depending taxonomy with the same name first. If this one is not found, the global taxonomy with the given id will be looked up and used instead.
How to configure access to the taxonomy administration
The taxonomy plugin uses the
configurations-rest-extension module to load
configuration values from a Settings document. The
configuration document TaxonomySettings that contains
the name of the user groups that are allowed to administrate taxonomies is
located in the folder /Settings/Options/Settings.
Additional configuration files with the same name can be put in the folder
Options/Settings (Relative paths will be concatenated with the root folder of the active site.). The entries of the files
will be added to the existing configuration. Below the default taxonomy
settings are shown.
<Struct xmlns="http://www.coremedia.com/2008/struct" xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink">
<StringListProperty Name="administrationGroups">
<String>global-manager</String>
</StringListProperty>
</Struct>