Studio User Manual / Version 2412.0
Table Of ContentsCoreMedia CMS provides a powerful and complex rights system for access management. However, as a Studio editorial user, you need to keep only five points in mind:
Content items may exist, but they are invisible to you because of your permissions.
Content items may exist that you can see but not edit.
Links to content items may be displayed, but you may be unable to view or edit the actual content. Instead of the content name you will see the lock icon and a text "Element name not visible".
Content items may exist that you may not publish.
Content items may exist that you cannot edit, because they are currently being edited by another user.
For administration of users and groups, you need to know the meaning of rights and rules and groups. See Section 3.15, “User Administration” in Content Server Manual for a more comprehensive and technical description of rights, rules, users and groups.
Rights define certain permissions on CoreMedia resources, to edit or publish content, for example. All the rights
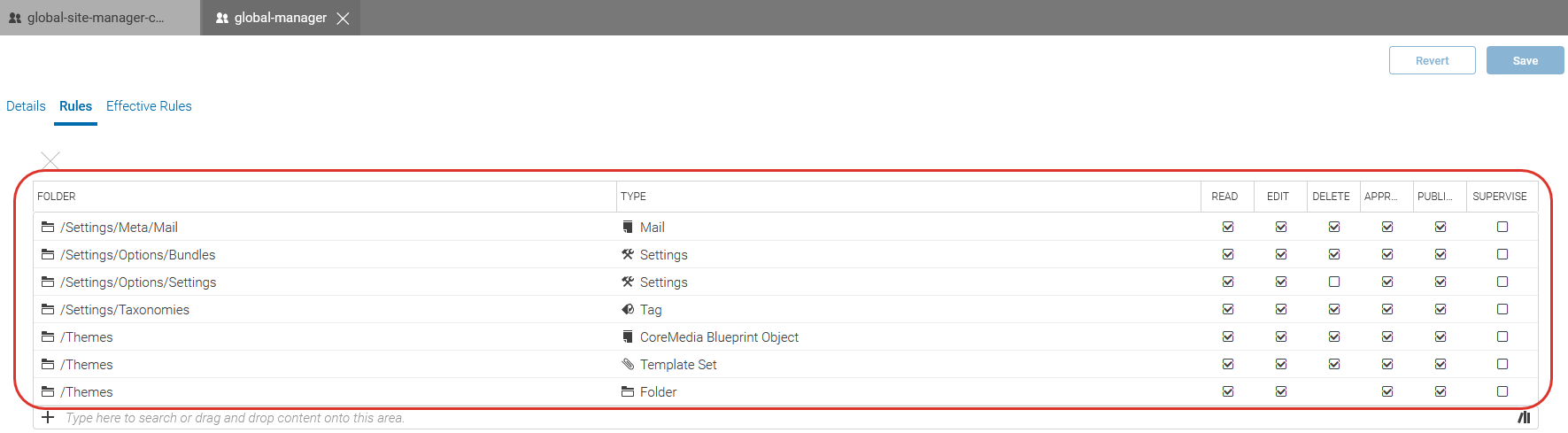
attached to a certain resource define a so called rule. Figure 2.38, “
Rules attached to a group
” shows some rules attached to the
global-manager group. The group has, for example, Read, Edit, Delete, Approve and Publish rights
on content of type Settings below the /Settings/Options/Bundles and
/Settings/Options/Settings folders.
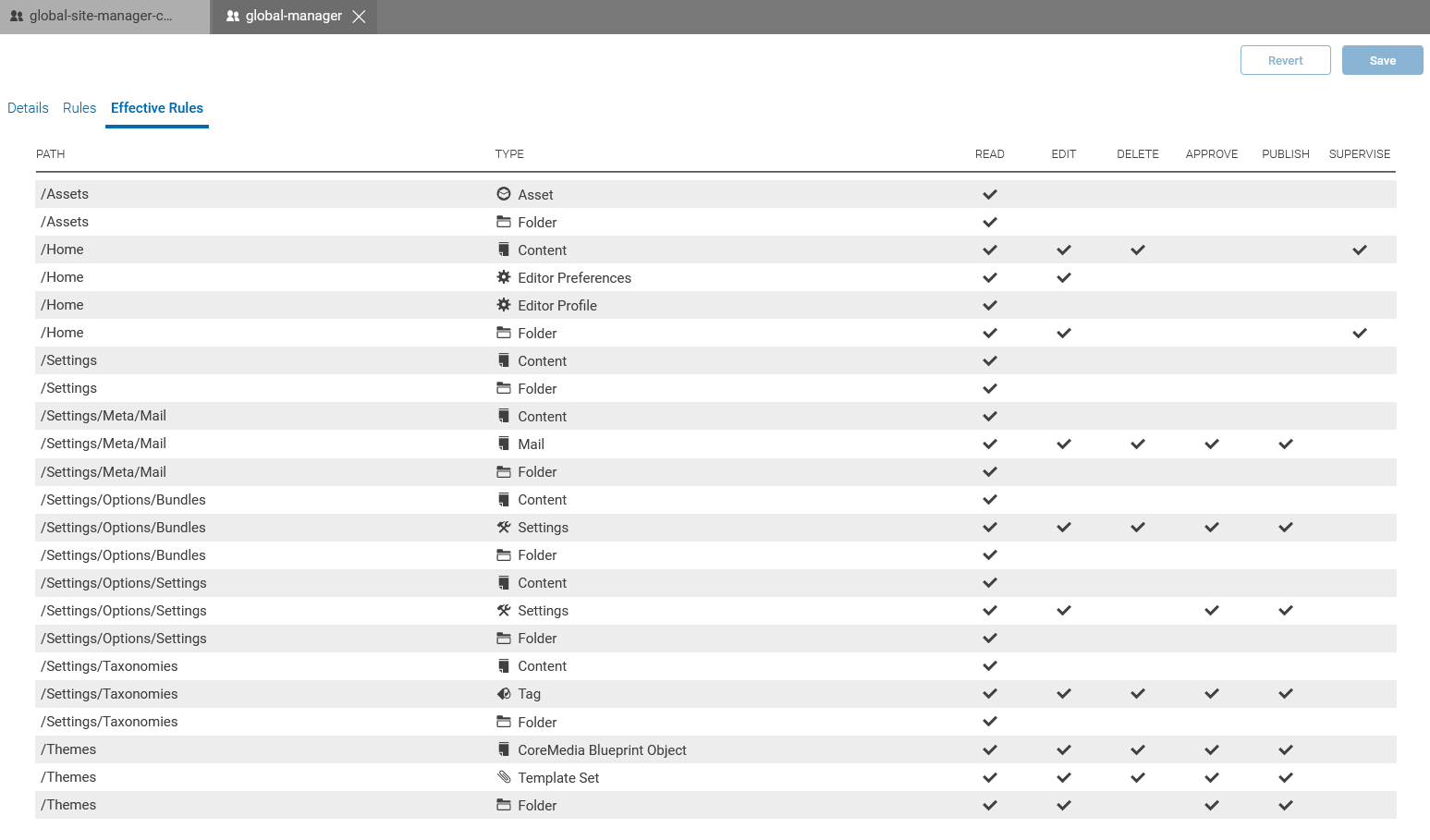
Groups have rules attached and can be members of other groups. A group which is a member of another group has all the rules of its parent groups. However, when a subgroup defines its own rules on a resource, this definition overwrites the definition from the parent group. You can check all the rules that apply to a group in the Effective Rules tab.
If a rule is applied to content types in a directory, the current rights structure for the particular group is passed on to the content items in subdirectories. If another rule should apply in a subdirectory it has to be created explicitly for the particular content types. For available rights and their impact see Section 3.15.2, “User Rights Management” in Content Server Manual.
If a user possesses different rights for a resource due to belonging to multiple groups, these rights are additively combined.
Example:
|
User |
Group |
Directory |
READ |
EDIT |
DELETE |
APPROVE |
PUBLISH |
GRANT |
FOLDER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
UserA |
Sport |
/News |
x | ||||||
|
UserA |
Politics |
/News |
x |
x |
x |
Table 2.6. Example groups
User A has READ, EDIT and DELETE rights for the CoreMedia directory /News, since the rights of
the groups add.
A user can be a member of several groups and inherits all rules of these groups. You can check all the rules that apply to a user in the Effective Rules tab.
|
Right |
Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
READ |
Read content names, content items content and folder names. | ||
|
EDIT |
Create, check out, check in, rename, move and save content items. Create subfolders, rename, move and delete a folder. | ||
|
DELETE |
Mark and unmark a content item for deletion, move an item to trash. For folders, you can not set the DELETE right, because it is included in the EDIT right. | ||
|
APPROVE |
Approve, disapprove a content item or folder. | ||
|
PUBLISH |
Publish a resource. | ||
|
SUPERVISE |
Check in a content item from a different user, grant new rights. |
Table 2.7. Group rights